We support countries to implement principles that conserve biodiversity, benefit local communities and enable them to diversify their export base through sustainable trade.
- What is BioTrade and why it matters
Biodiversity is the natural capital base for a sustainable economy. The conservation of biodiversity and the sustainable use and trade of biodiversity-derived products and services can provide countries valuable opportunities for economic development and improvement of livelihoods.
To capture this opportunity, in 1996 UNCTAD launched the BioTrade Initiative to support the objectives of the Convention on Biological Diversity. Since then, the Initiative has developed a unique portfolio of global, regional and country programmes as well as a network of partners and practitioners.
BioTrade is when a product or service sourced from biodiversity is commercialized and traded in a way that respects people and nature.
The BioTrade Principles and Criteria developed by UNCTAD is a set of guidelines for businesses, governments and civil society wishing to support the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity, as well as the fair and equitable sharing of benefits through trade. Today they are implemented and fostered by government organizations, business associations, NGOs, and companies in nearly 100 countries.
BioTrade has been considered in the processes of international agreements such as the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES).
- Our mandate
UNCTAD has a mandate to work on sustainable trade and biodiversity.
- In 1996, the BioTrade Initiative was launched as the UNCTAD response to implementing the 1992 Earth Summit’s Agenda 21, the blueprint for sustainable development action into the twenty-first century.
- In 2000, at the UNCTAD 10 Conference, Member States granted a mandate to support developing countries in strengthening their capacity to design and implement mutually supportive trade and biodiversity policies and measures at all levels.
- In 2016, the UNCTAD 14 Conference requested UNCTAD to “Promote sustainable trade in biodiversity products and services to strengthen the sustainability of biodiversity and foster sustainable growth, in close cooperation with other relevant agencies where appropriate;” (the Nairobi Maafikiano, (para. 76 (q)).
BioTrade was intended to serve as the platform through which UNCTAD would contribute to the implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, especially SDG 15: Life on land.
- In 2021, this mandate was expanded at the UNCTAD 15 Conference which noted that biodiversity loss and environmental degradation have become key challenges for sustainable development (the Bridgetown Covenant (para. 65; 73 and 127 (II)).
The UNCTAD BioTrade Initiative currently supports governments in achieving their commitments related to multilateral environmental agreements such as the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), the Aichi Biodiversity Targets, and the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES).
The conceptual framework guiding BioTrade interventions on the ground, the BioTrade Principles and Criteria, were updated in 2020 to be more closely aligned with key multilateral environmental agreements, notably CBD and CITES.
- In 1996, the BioTrade Initiative was launched as the UNCTAD response to implementing the 1992 Earth Summit’s Agenda 21, the blueprint for sustainable development action into the twenty-first century.
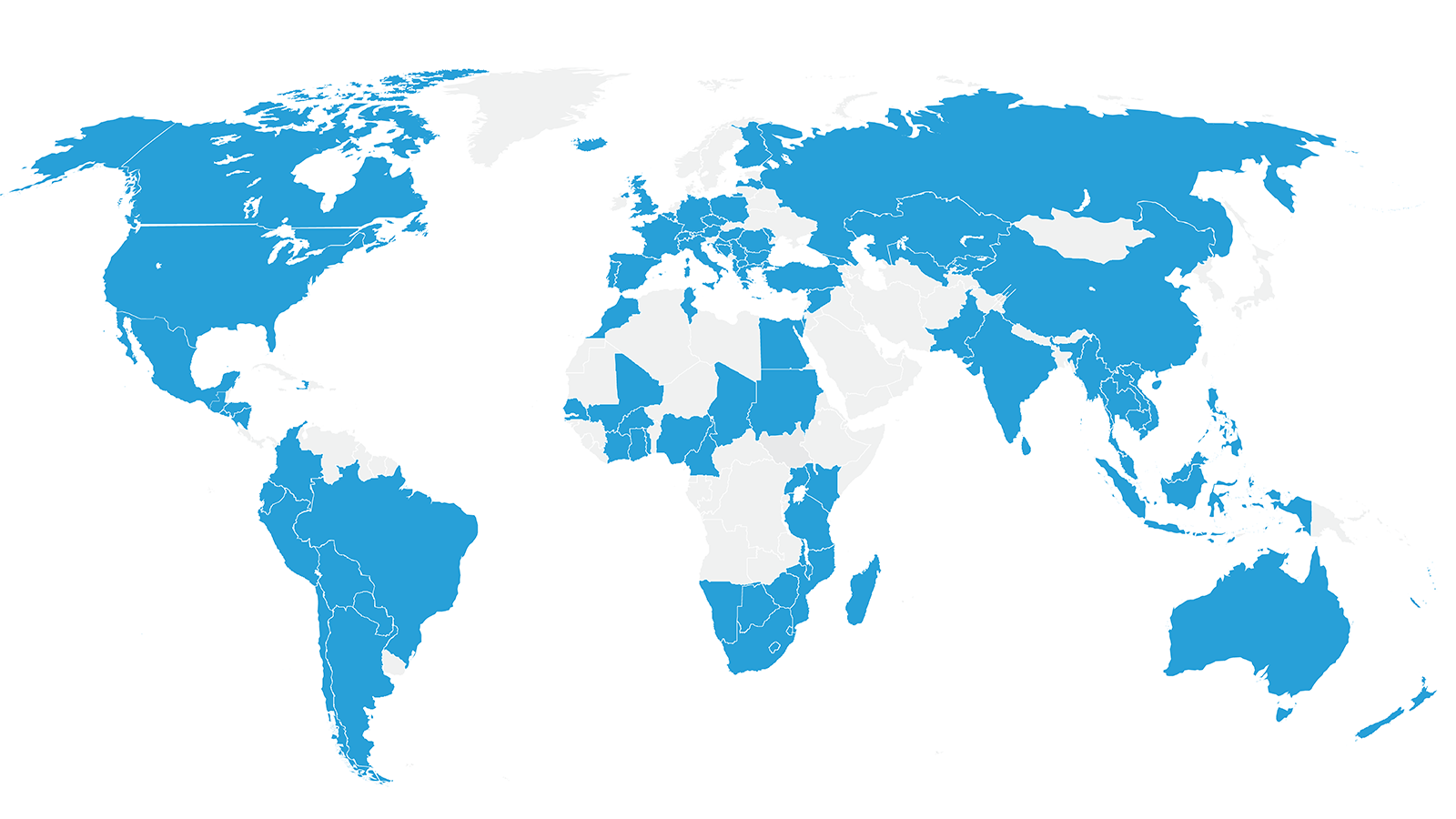
- BioTrade around the world
BioTrade is being implemented in approximately 100 countries.
News
Publications
BioTrade in action
Featured podcast
Ecosistemas en peligro: Por qué nuestro futuro depende de la protección de la biodiversidad
Related
Areas of work
- BioTrade Principles and Criteria
Sustainability criteria used to guide the activities of the BioTrade Initiative, and adopted by practitioners in over 100 countries. - Trade in biodiversity-based products
Data on imports and exports of biodiversity-based products and other relevant indicators. - BioTrade Knowledge Sharing & Self-Assessment Tool
Enabling BioTrade value chain actors to connect, access information and benchmark their sustainability performance. - Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework
An international agreement adopted in 2022 to guide global efforts to protect and restore biodiversity.






