BioTrade is defined as the collection, production, transformation, and commercialization of biodiversity-based goods and services that meet specific sustainability criteria.
These criteria - called the BioTrade Principles and Criteria (P&C) - have been developed and implemented since 2007 to guide the activities of the BioTrade Initiative and its programmes, partners and practitioners.
Today they have been adopted and are used by practitioners in approximately 100 countries.
Conceptual framework
The BioTrade principles and criteria for terrestrial, marine and other aquatic biodiversity-based products and services include seven principles:
- Conservation of biodiversity
- Sustainable use of biodiversity
- Fair and equitable sharing of benefits
- Socioeconomic sustainability
- Legal compliance
- Respect for actors' rights
- Right to use and access natural resources
To implement the BioTrade Principles and Criteria, UNCTAD adopted four different approaches:
- The “value chain approach”, which involves actors from all parts of the value chain working together to achieve agreed goals.
- The “adaptive management approach”, which allows for corrective measures to be adopted on the basis of ongoing monitoring of impacts.
- The “ecosystem approach”, which takes a holistic approach to ecological and social issues and the interactions and processes that make up production systems.
- The "sustainable livelihoods approach", which contributes to sustaining livelihoods, in particular of the poor and vulnerable populations.
Mandates, Principles and Approches 2020
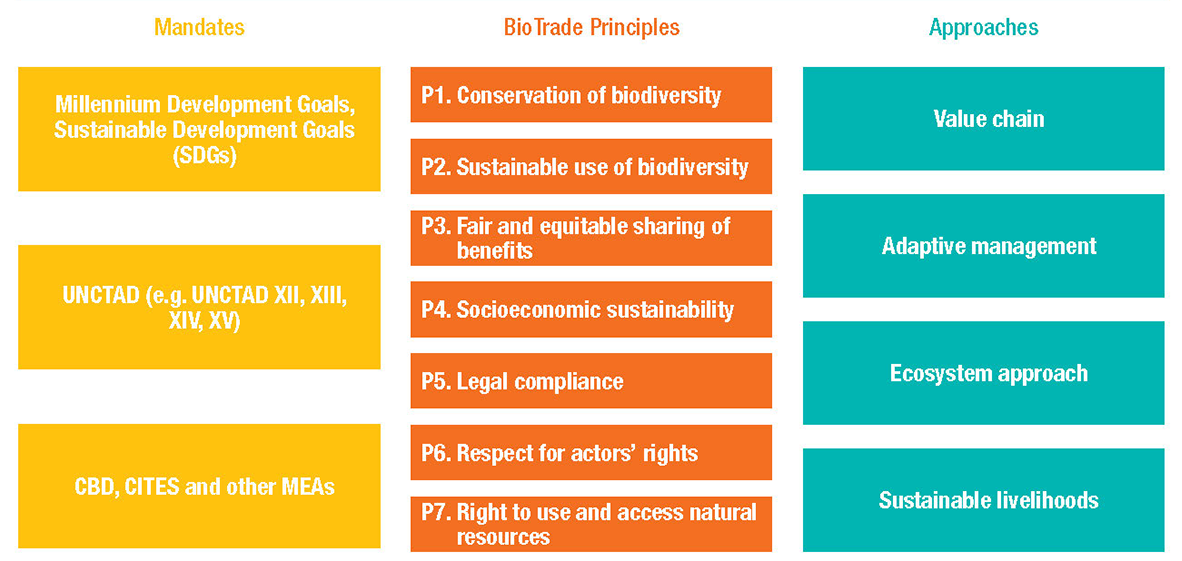
Adopted from UNCTAD, 2007
The BioTrade P&C can be applied in different contexts:
-
By government ministries or agencies evaluating, identifying and verifying good practices and guiding elements to be included in a policy and diversify the export base.
-
By companies to assess the social, economic and environmental impact of a project, company or supply chain.
-
By organizations wanting to integrate sustainable trade and biodiversity considerations into their activities.
The BioTrade P&C have recently been updated to address new challenges, evolving legal and policy frameworks. Building upon the experiences of and lessons learned by practitioners for more than 10 years, the 2020 BioTrade Principles and Criteria have provisions for emerging issues such as the climate emergency, expanded coverage to include additional sectors such as marine biodiversity and sustainable tourism, been aligned with recent international agreements and sustainability targets, such as the Sustainable Development Goals and the Paris Agreement on Climate Change.
Applying the BioTrade P&C means respecting biodiversity and becoming part of the solution for the biodiversity crises. While trade can be an indirect driver of biodiversity loss, when done sustainably it can support livelihoods and contribute to the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity. BioTrade contributes to the transformation needed to implement the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework and should therefore be part of this framework.
The updated BioTrade P&C and the BioTrade Knowledge Sharing and Self-Assessment Tool were developed under the Global BioTrade programme: Linking trade, biodiversity and sustainable development launched by UNCTAD in 2018 with the support of the Swiss State Secretariat for Economic Affairs SECO.
2020 BioTrade Principles and Criteria
The BioTrade P&C have recently been updated to address new challenges, evolving legal and policy frameworks.
Building upon the experiences of and lessons learned by practitioners for more than 10 years, the 2020 BioTrade Principles and Criteria have provisions for emerging issues such as the climate emergency, expanded coverage to include additional sectors such as marine biodiversity and sustainable tourism, been aligned with recent international agreements and sustainability targets, such as the Sustainable Development Goals and the Paris Agreement on Climate Change.
Applying the BioTrade P&C means respecting biodiversity and becoming part of the solution for the biodiversity crises. While trade can be an indirect driver of biodiversity loss, when done sustainably it can support livelihoods and contribute to the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity.
BioTrade contributes to the transformation needed to implement the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework and should therefore be part of this framework.
The updated BioTrade Principles and Criteri and the BioTrade Knowledge Sharing and Self-Assessment Tool were developed under the Global BioTrade programme: Linking trade, biodiversity and sustainable development launched by UNCTAD in 2018 with the support of the Swiss State Secretariat for Economic Affairs SECO.
BioTrade Knowledge Sharing and Self-Assessment Tool
Enabling BioTrade value chain actors to connect, access information and benchmark their sustainability performance

The tool showcases information related to biodiversity-based initiatives, allowing users to connect with different value chain actors and benchmark their sustainability practices against the BioTrade Principles and Criteria. The BioTrade Knowledge Sharing and Self-Assessment Tool has been jointly developed by UNCTAD and ITC.