Illicit Financial Flows
Illicit financial flows (IFFs) drain resources from development not only when they leave a country (outflows), but also when they enter a country (inflows), they can have detrimental impact by fuelling money laundering and corruption thus undermining the rule of law and the stability of markets.
Illicit Financial Flows
Illicit financial flows (IFFs) drain resources from development not only when they leave a country (outflows), but also when they enter a country (inflows), they can have detrimental impact by fuelling money laundering and corruption thus undermining the rule of law and the stability of markets.
UNCTAD and the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) as custodians of SDG indicator 16.4.1, “total value of inward and outward IFFs”, collaborate with United Nations Regional Commissions and other experts within the Task Force on the Statistical Measurement of IFFs. As a result, UNCTAD and UNODC published a Conceptual Framework for the Statistical Measurement of Illicit Financial Flows endorsed by the United Nations Statistical Commission (UNSC) in March 2022.
The Conceptual Framework provides the first ever UN wide definition of IFFs for statistical purposes: Financial flows that are illicit in origin, transfer or use, that reflect an exchange of value and that cross country borders.
In addition, in May 2021, UNCTAD finalised a draft of Methodological Guidelines to Measure Tax and Commercial IFFs for pilot testing, aimed at statistical and other national authorities with a mandate to collect and access relevant information.
The world needs comparable and reliable statistics on IFFs to shed light on the activities, sectors and channels most prone to illicit finance, pointing to where actions should be undertaken as a priority to curb these flows. First official estimates on IFFs are now available, covering some crime-related IFFs for the first member States.
UNCTAD, UNODC and UN Regional Commissions are addressing a growing need for global cooperation and strengthening of existing work avenues to tackle IFFs and the activities that underlie their occurrence in a global project and provide further support to member States.
An overview of our work
An overview of our work on defining, estimating and disseminating statistics on illicit financial flows.
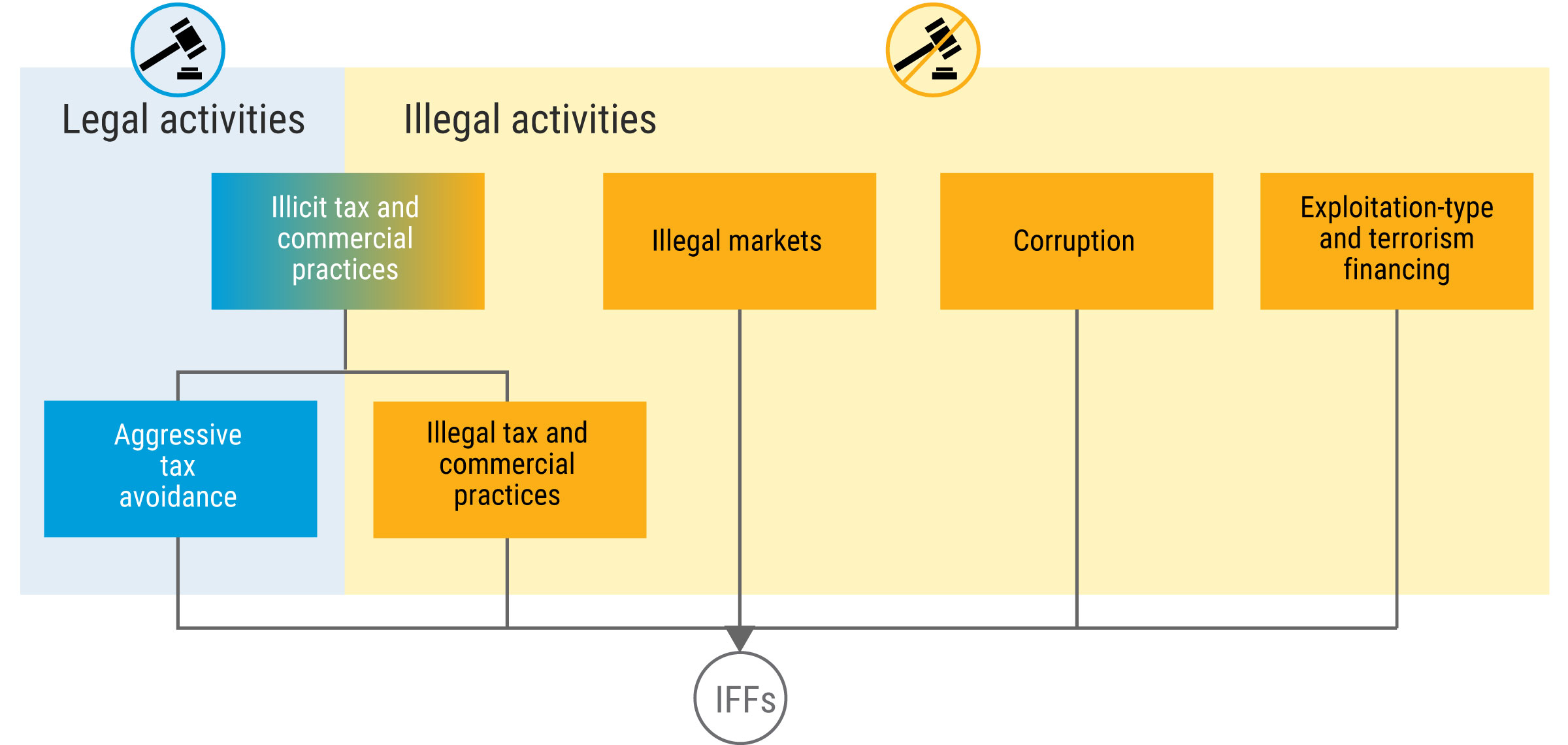
Activities that may generate illicit financial flows
Pilot countries measuring IFFs, by type of IFFs
The designations employed and the presentation of material on this map do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Secretariat of the United Nations and/or on the part of the countries mentioned on it, concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. (ST/AI/189/Add.25/Rev.1). The information shown is this map is for information purposes only and should be not be considered as any form of endorsement by the United Nations and does not create any legal rights or obligations for any Member State or any of the organs thereof.
News
Related
SDG Pulse
- Measuring illicit financial flows for stronger domestic resources
Progress by UNCTAD and UNODC as custodians of SDG indicator 16.4.1 on illicit financial flows
Projects
- Measuring and Curbing Illicit Financial Flows
- Measurement of IFFs and policy formulation in Ghana, Namibia and Zambia
- Measuring illicit financial flows in the Asia-Pacific region
- Statistics on illicit financial flows in Africa
- Developing an indicator on illicit financial flows in Latin America
- Egypt SDGs financing strategy
Events & meetings
Documents
18 Oct 2022
Promotion of international cooperation to combat illicit financial flows and strengthen good practices on assets return to foster sustainable development: Achievements, challenges and way forward
Paper prepared by UNCTAD, in consultation with UNODC, in compliance with A/RES/76/196
EnglishReporting files
Together, these files form a coherent reporting package for SDG indicator 16.4.1 on illicit financial flows (IFFs).
The data template covers the reporting of estimates on IFFs from trade misinvoicing, aggressive tax avoidance and tax evasion.
The two accompanying Word templates facilitate the reporting of metadata on trade misinvoicing and aggressive tax avoidance estimates. They are used to complement data information reported in the Excel file and to clarify methodological steps.
- UNCTAD SDG 16.4.1 metadata reporting template – Trade misinvoicing (English / French)
- UNCTAD SDG 16.4.1 metadata reporting template – Aggressive tax avoidance (English / French)
Data submitted by countries to UNCTAD through the Excel form will be transmitted to the UN Statistics Division for SDG reporting. The accompanying metadata may be used to supplement and contextualize related information.




