Our mandate
UNCTAD first obtained a mandate on oceans and seas at the UNCTAD 14 Conference (Paragraph 100(t) of the Nairobi Maafikiano), which was expanded at UNCTAD 15 Conference (Paragraphs 76 and nn of the Bridgetown Covenant).
At its sixteenth session (UNCTAD 16), held in Geneva in October 2025, UNCTAD received a renewed mandate to support developing countries in harnessing the ocean economy for sustainable development. The Geneva Consensus explicitly states:
"UNCTAD should continue to support developing countries to sustainably harness the ocean economy and the effective implementation of relevant international commitments on maritime transport and ocean governance as well as in the design and implementation of economic development strategies for the conservation and sustainable use of oceans and their resources."(TD(XVI)/PC/1, para. 80.52)
This renewed mandate ensures UNCTAD will continue to promote inclusive and sustainable ocean-based economic strategies, aligned with trade-related targets of SDG 14 and other global frameworks.
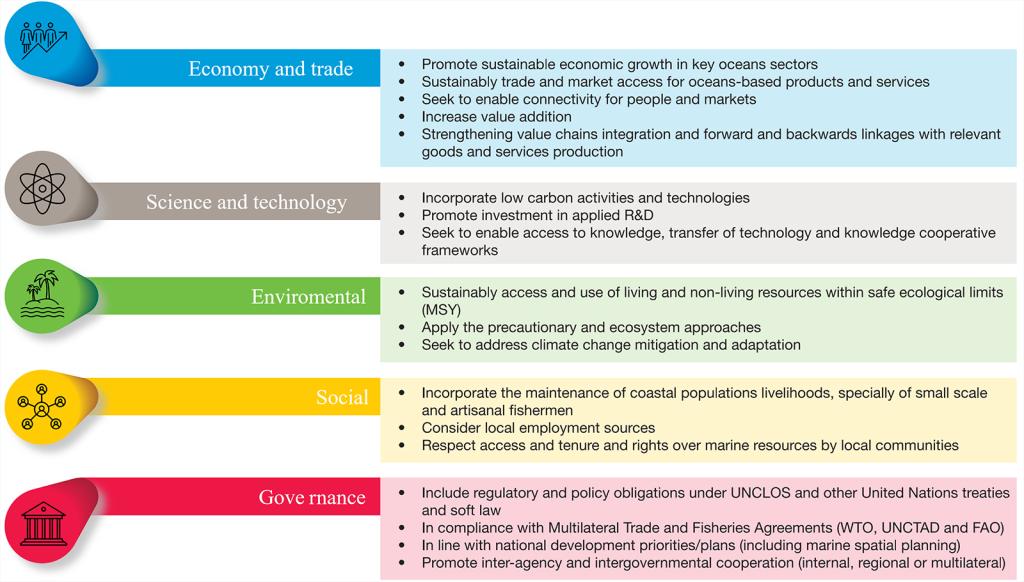
Five pillars of the oceans economy
News
Sustainable Ocean Economy Classification
The identification of sustainable ocean economy sectors and their respective Harmonized System codes was conducted in the UNCTAD report "Towards a harmonized international trade classification for the development of sustainable ocean-based economies".
A dataset on Ocean Trade is now available in the UNCTADstat Data Center.
Publications
Featured videos
Featured Podcast
Deep sea mining: Necessary innovation or environmental risk?
Related
Special initiative
Projects
12 – 13 March 2026
National workshop on enhanced statistics for evidence-based climate action in maritime trade, transport and fisheries in Belize
9 – 18 December 2025
E-training course: Emerging issues at the interplay between trade and sustainable development
4 – 5 December 2025
National workshop on enhanced statistics for evidence-based climate action in maritime trade, transport and fisheries in Barbados
19 November 2025