As part of its work on monitoring and analysing commodity markets and trends, the UNCTAD Infocomm team is launching a new study ("e-profile") on the cotton sector. Infocomm, a technical cooperation project aimed at improving the transparency of the commodities market through knowledge management tools, offers an electronic portal of commodity information. As with other commodity studies already available on the portal, the latest one on cotton focuses on 10 main aspects of the sector: characteristics, cultivation, quality, uses, market, marketing chain, companies, technology, prices and economic policies.
According to the International Cotton Advisory Committee (ICAC), world cottonseed production is expected to reach 25.4 millions tonnes for the year 2004/05, up 23% (the largest year-to-year increase ever) from last season, and is likely to outpace consumption by 2.6 million tonnes. Cotton is grown primarily in four countries - China, the United States, India and Pakistan - which together account for about two thirds of world production.
The new e-profile should make it easier to understand the challenges facing each segment of the cotton production and marketing chain as a result of current economic, trade and social developments. One of the most important such developments is the recent WTO decision on the US-Brazil dispute over US subsidies of upland cotton, which the study helps to put in perspective.
Of the 100-plus countries counted as cotton growers this year, 80 are developing nations and 28 are classified by the UN as least developed countries (LDCs). Cotton is of great importance for developing nations, particularly in western and central Africa, where 10 million people depend directly on the sector for their income. Of the rural populations in Benin and Mali, for example, 45% and 40% respectively depend either directly or indirectly on cotton, which accounts for about a third of all exports.
![[type here the Title of the graph]](/sites/default/files/inline-images/pr05013f1_fr.gif)
In order to arrive at the best decisions, especially where national, regional and international policies are concerned, the functioning of each sector must be fully understood. And to optimize the economic efficiency of the production and marketing chain, the market fundamentals influencing the main economic actors and the cotton sector as a whole have also to be considered. Trends in the cotton sector affect not just the US and Brazilian economies but also those of countries in Africa, Eastern Europe and Asia. The UNCTAD study helps to explain current developments and also elucidates specific problems through strategically chosen links to other websites. Liberalization in the Africa cotton sector, for example, has turned market structures upside down and is likely to contribute to a rise in input prices. This in turn has an impact on yield and hence on the competitiveness of cotton farmers (who tend to be major staple food producers as well). Technological changes now under way in the sector should also not be underestimated, such as the production of genetically modified cotton, which already accounts for one fourth of the world´s cottonfields (vs. just 2% in 1997).
Trends in cotton prices (Cotlook A-Index, US cents/lb.) and net exports from China over the period 1980/81-2003/04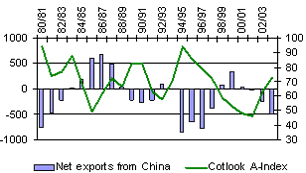
Source: UNCTAD
Cotton was the world´s leading source of fibres through the first half of the 20th century, and prior to the First World War accounted for more than 81% of all uses of fibres. That share began to decline with the development of artificial and synthetic fibres. Today, cotton represents less than 40% of fibre consumption worldwide, while synthetics account for more than half (vs. 5% in the 1960s). Since the early 1980s, another factor has been upsetting the balance in the cotton trade: China. This country plays a crucial role in international cotton price-setting, particularly because of the uncertainties surrounding its trade position, both as importer and exporter.
Infocomm: UNCTAD electronic portal on commodities
UNCTAD´s Infocomm e-portal has become increasingly visible in the commodity information field, boasting 4.4 million hits and more than 129,000 interactive sessions in January 2005 alone, or twice as many visitors as a year ago. Infocomm has also published 20 other monographs online (in French, English and Spanish), containing objective, up-to-date information on the following categories:
- Agricultural products (citrus fruits, cashew nut, banana, wheat, timber, jute, shea-nut, olive oil, pepper, rice, sugar and tobacco);
- Beverages (cocoa and tea);
- Metals and minerals (iron/steel, nickel, palladium, platinum and zinc); and
- Energy (natural gas and oil).


