
The present edition of the Review of Maritime Transport takes the view that the long-term growth prospects for seaborne trade and maritime businesses are positive. There are ample opportunities for developing countries to generate income and employment and help promote foreign trade.
Seaborne trade
In 2015, estimated world seaborne trade volumes surpassed 10 billion tons - the first time in the records of UNCTAD. Shipments expanded by 2.1 per cent, a pace notably slower than the historical average. The tanker trade segment recorded its best performance since 2008, while growth in the dry cargo sector, including bulk commodities and containerized trade in commodities, fell short of expectations. While a slowdown in China is bad news for shipping, other countries have the potential to drive further growth. South-South trade is gaining momentum, and planned initiatives such as the One Belt, One Road Initiative and the Partnership for Quality Infrastructure, as well as the expanded Panama Canal and Suez Canal, all have the potential to affect seaborne trade, reshape world shipping networks and generate business opportunities. In parallel, trends such as the fourth industrial revolution, big data and electronic commerce are unfolding, and entail both challenges and opportunities for countries and maritime transport.
Maritime businesses
The world fleet grew by 3.5 per cent in the 12 months to 1 January 2016 (in terms of dead-weight tons (dwt)). This is the lowest growth rate since 2003, yet still higher than the 2.1 per cent growth in demand, leading to a continued situation of global overcapacity. Different countries participate in different sectors of the shipping business, seizing opportunities to generate income and employment. As at January 2016, the top five ship owning economies (in terms of dwt) were Greece, Japan, China, Germany and Singapore, while the top five economies by flag of registration were Panama, Liberia, the Marshall Islands, Hong Kong (China) and Singapore. The largest shipbuilding countries are China, Japan and the Republic of Korea, accounting for 91.4 per cent of gross tonnage constructed in 2015. Most demolitions take place in Asia; four countries - Bangladesh, India, Pakistan and China - accounted for 95 per cent of ship scrapping gross tonnage in 2015. The largest suppliers of seafarers are China, Indonesia and the Philippines.
Freight rates and maritime transport costs
In 2015, most shipping segments, except for tankers, suffered historic low levels of freight rates and weak earnings, triggered by weak demand and oversupply of new tonnage. The tanker market remained strong, mainly because of the continuing and exceptional fall in oil prices. In the container segment, freight rates declined steadily, reaching record low prices as the market continued to struggle with weakening demand and the presence of ever-larger container vessels that had entered the market throughout the year. In an effort to deal with low freight rate levels and reduce losses, carriers continued to consider measures to improve efficiency and optimize operations, as in previous years. Key measures included cascading, idling, slow steaming, and wider consolidation and integration, as well as the restructuring of new alliances.
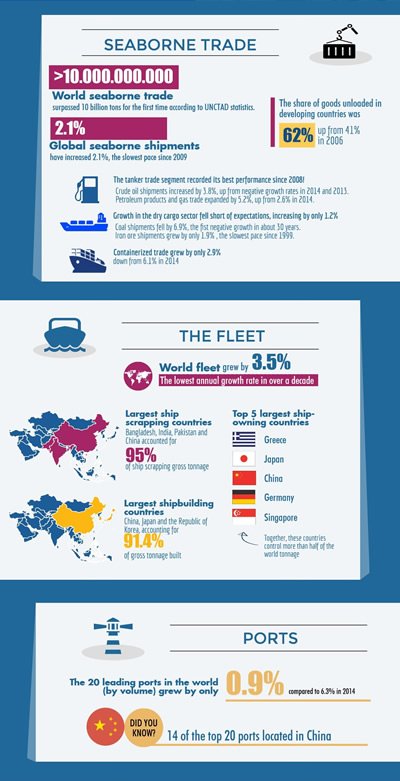
Ports
The overall port industry, including the container sector, experienced significant declines in growth, with growth rates for the largest ports only just remaining positive. The 20 leading ports by volume experienced an 85 per cent decline in growth, from 6.3 per cent in 2014 to 0.9 per cent in 2015. Of the seven largest ports to have recorded declines in throughput, Singapore was the only one not located in China. Nonetheless, with 14 of the top 20 ports located in China, some ports posted impressive growth, and one (Suzhou) even grew by double digits. The top 20 container ports, which usually account for about half of the world's container port throughput and provide a straightforward overview of the industry in any year, showed a 95 per cent decline in growth, from 5.6 per cent in 2014 to 0.5 per cent in 2015.
Legal issues and regulatory developments
During the period under review, important developments included the adoption of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development in September 2015 and the Paris Agreement under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change in December 2015. Their implementation, along with that of the Addis Ababa Action Agenda, adopted in July 2015, which provides a global framework for financing development post-2015, is expected to bring increased opportunities for developing countries.
Among regulatory initiatives, it is worth noting the entry into force on 1 July 2016 of the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea amendments related to the mandatory verification of the gross mass of containers, which will contribute to improving the stability and safety of ships and avoiding maritime accidents.
At the International Maritime Organization, discussions continued on the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions from international shipping and on technical cooperation and transfer of technology particularly to developing countries. Continued enhancements were made to regulatory measures in the field of maritime and supply chain security and their implementation.
Areas of progress included the implementation of authorized economic operator programmes and an increasing number of bilateral mutual recognition agreements that will, in due course, form the basis for the recognition of authorized economic operators at a multilateral level. As regards suppression of maritime piracy and armed robbery, in 2015, only a modest increase of 4.1 per cent was observed in the number of incidents reported to the International Maritime Organization, compared with 2014.


